
17 Goals for People, for Planet
The STEMarts Curriculum aligns to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals which address current global challenges. Through this partnership students know that they are working on meaningful solutions toward building a sustainable future for all. The Sustainable Development Goals are a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet and improve the lives and prospects of everyone, everywhere. The 17 Goals were adopted by all UN Member States in 2015, as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development which set out a 15-year plan to achieve the Goals. The BioSTEAM program addresses the following sustainable development goals.
Goal #17 PARTNERSHIPS FOR THE GOALS: Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development.
Goal #18 SPACE FOR ALL: HOW SPACE CAN BE USED IN SUPPORT OF THE 2030 AGENDA FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Goal #11 SUSTAINABLE CITIES AND COMMUNITIES: Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
GOAL #4: QUALITY EDUCATION: Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all.
Next Generation Science Standards
STEMarts curriculum aligns with the Next Generation Science standards (NGSS), and the P21 Framework for 21st Century Learning.
The STEMarts International Design Challenge ‘Space for Earth- Space for All’
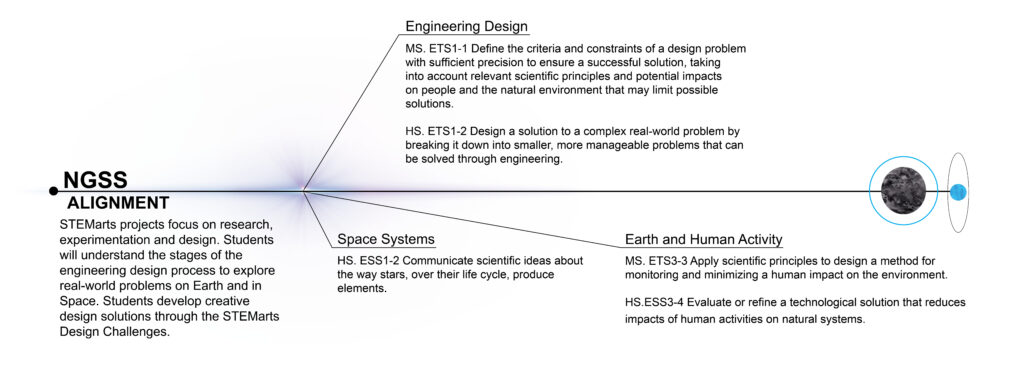
MS. ETS1-1 Engineering Design: Define the criteria and constraints of a design problem with sufficient precision to ensure a successful solution, taking into account relevant scientific principles and potential impacts on people and the natural environment that may limit possible solutions.
MS-ESS3-3 Earth and Human Activity: Apply scientific principles to design a method for monitoring and minimizing a human impact on the environment.
HS.ETS1-2 Engineering Design: Design a solution to a complex real-world problem by breaking it down into smaller, more manageable problems that can be solved through engineering.
HS.ESSS3-4 Earth and Human Activity: Evaluate or refine a technological solution that reduces impacts of human activities on natural systems. Space Systems: Communicate scientific ideas about the way stars, over their life cycle, produce elements.
The BioMachine Design Challenge is designed to LS4.D Biodiversity & Humans.
The P21 Framework for 21st Century Learning was developed with input from educators, education experts, and business leaders to define and illustrate the skills, knowledge, expertise, and support systems that students need to succeed in work, life, and citizenship. The Framework continues to be used by thousands of educators and hundreds of schools in the U.S. and abroad to put 21st century skills at the center of learning. All elements of the Framework are critical to ensure 21st century readiness for every student.
Below are key definitions and core ideas from the NGSS that are investigated through this curriculum. You can share these core ideas with students to inform their design thinking.
National Core Arts Standards
STEMarts programming harmoniously integrates with the National Core Arts Standards, weaving together the core principles of creating, performing/presenting/producing, responding, and connecting. Our curriculum encourages students to actively create original works, whether through digital media, augmented reality, or other artistic mediums, fostering self-expression and innovation. Through performances, presentations, and productions, students showcase their creations, honing their skills in communication and presentation. Furthermore, our program encourages students to critically respond to art, technology, and scientific concepts, cultivating analytical thinking and reflection. By fostering connections between STEM disciplines and the arts, STEMarts empowers students to see the interconnectedness of knowledge domains, facilitating a holistic understanding of the world and their place within it.
Definitions of Technology, Engineering, and Applications of Science
- Technology is any modification of the natural world made to fulfill human needs or desires.
- Engineering is a systematic and often iterative approach to designing objects, processes, and systems to meet human needs and wants.
- An Application of Science is any use of scientific knowledge for a specific purpose, whether to do more science; to design a product, process, or medical treatment; to develop a new technology; or to predict the impacts of human actions.
NEXT GENERATION SCIENCE STANDARDS
Core Idea ETS1: Engineering DesignETS1.A: Defining and Delimiting an Engineering Problem ETS1.B: Developing Possible Solutions ETS1.C: Optimizing the Design Solution |
|---|
In ETS1 Middle school students engage in the engineering design process in a way that is personally relevant and on an appropriate scale. In ETS1 High school students are called on to engage in the engineering design process to address complex real-world problems that account for societal needs and wants and use practical criteria. STEMarts Objectives
|
Core idea ETS2: Links Among Engineering, Technology, Science, and SocietyETS2.A: Interdependence of Science, Engineering, and Technology ETS2.B: Influence of Engineering, Technology, and Science on Society and the Natural World |
STEMarts Objectives
|
NGSS Crosscutting Concepts woven through the STEMarts projects provide students with connections that are related across the differing areas of disciplinary content and can enrich their application of practices and their understanding of core ideas in science. These same crosscutting concepts are explored in the STEMarts sci-art approach through visual, auditory and linguistic explorations. •Patterns •Cause & effect •Proportion & Quantity •Systems & System Models •Energy & Matter •Structure and Function •Stability & Change |
21ST CENTURY LEARNING SKILLS
The P21 Skills Framework promotes an understanding of academic content at much higher levels by weaving 21st century interdisciplinary themes into key subjects: •Global Awareness •Financial, Economic, Business and Entrepreneurial Literacy. •Civic Literacy•Health Literacy •Environmental Literacy |
|---|
Overview
STEMarts objective:
|
Learning and Innovation SkillsLearning and innovation skills increasingly are being recognized as the skills that separate students who are prepared for increasingly complex life and work environments in the 21st century, and those who are not. A focus on creativity, critical thinking, communication and collaboration is essential to prepare students for the future. STEMarts objectives
|
Information, Media, and Technology SkillsToday we live in a technology and media-suffused environment with: 1) access to an abundance of information, 2) rapid changes in technology tools, and 3) the ability to collaborate and make individual contributions on an unprecedented scale. To be effective in the 21st century, citizens and workers must be able to create, evaluate, and effectively utilize information, media, and technology. Objective:Through the STEMarts WIKI platform students must learn to search through hyperlinked articles, videos and research papers to gather the information about the proposed project. They develop scientific literacy as they check and cite sources on scientific content. Life and Career SkillsToday’s students need to develop thinking skills, content knowledge, and social and emotional competencies to navigate complex life and work environments. P21’s essential Life and Career Skills include: •Flexibility and Adaptability •Initiative and Self-Direction. •Social and Cross-Cultural Skills •Productivity and Accountability •Leadership and Responsibility |
